Infographic
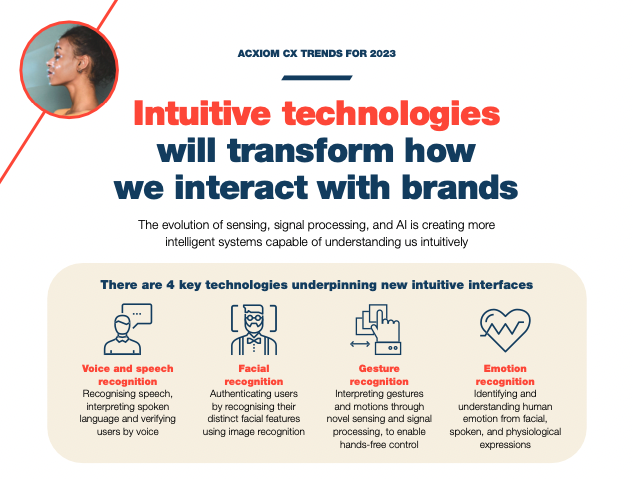
The evolution of sensing, signal processing, and Al is creating more intelligent systems capable of understanding us intuitively
What Is It?
The smartphone transformed the way we communicate with businesses and each other. Now, intuitive technologies that can interpret and understand our intentions look set to transform how we interact with products and services, as well as the technologies that underpin them.
Intuitive technologies are already here in a variety of shapes and forms:
-

Voice & speech recognition
Speech recognition identifies spoken words and uses intelligent back-end technologies such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) to make sense of those words. This allows us, for example, to call a friend or play a song just by asking our smart device. Voice recognition is a biometric technology that identifies a specific voice, and it can be used for identity authentication. These two technologies are often used together in digital assistants.
-

Facial recognition
Facial recognition enables us to unlock devices and accounts without having to enter passwords, providing a more intuitive way to verify our identity.
Apple’s FaceID, for instance, allows users to unlock their iPhone or iPad just by glancing at it and can also be used to make purchases, authorize payments, and sign into apps.
-
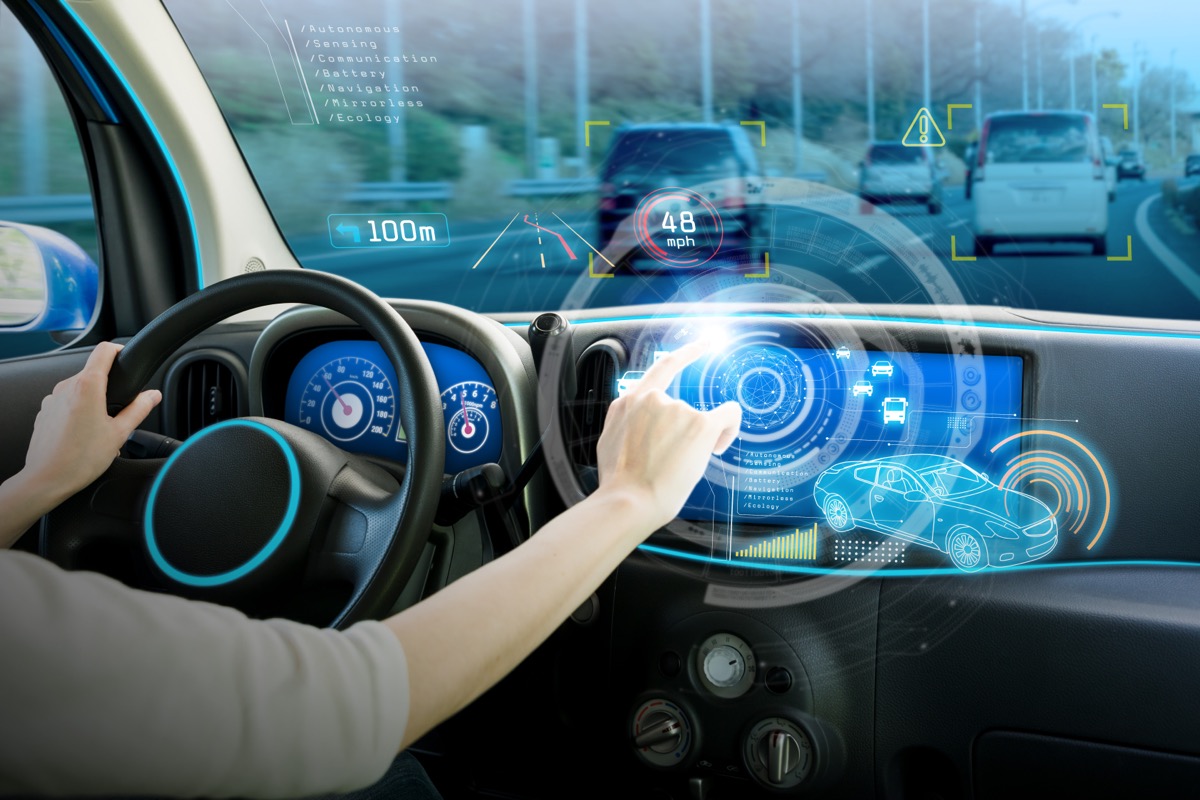

Gesture recognition
Gesture recognition enables us to perform certain tasks, actions, or functions by making specific, predefined motions or gestures.
The value of gesture recognition is demonstrated most clearly by touchless controls in the automotive sector.
-
Emotion recognition
Advances in computer vision mean digital systems can passively recognize and understand human feelings and emotions, enabling them to adapt and respond to the user’s emotional state without active input. The field of sentiment analysis is rapidly evolving, with an increasing number of technologies trying to capture a customer’s perceived mood, e.g. delight or frustration, and using that as a first- party data point to direct interactions.
Case Study
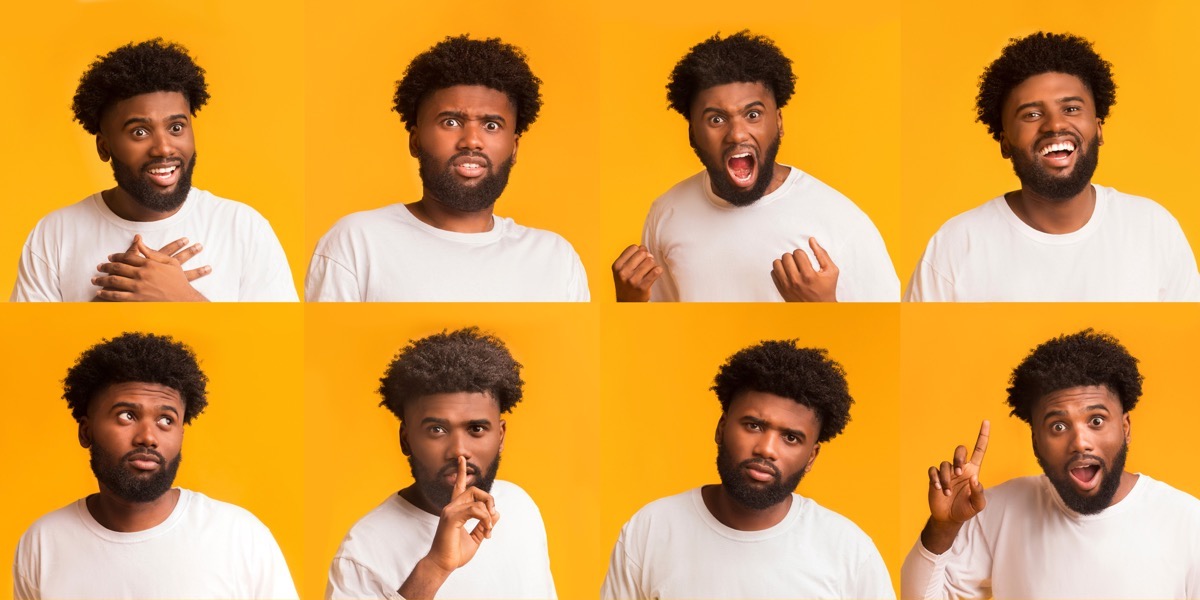

Gesture recognition: making Android more accessible for everyone
Millions of people are already using digital assistants like Siri or Google Assistant to perform tasks and navigate their phones using only their voice. Late last year, Google rolled out two new innovations which make Android more accessible for everyone. Camera Switches1 turns the front-facing camera into a sensor that detects facial gestures, enabling anyone to use eye movements (look left, look right, look up) and facial gestures (smile, raise eyebrows, and open your mouth) to navigate their phone. Project Activate takes this one step further and enables users to use facial gestures to active customized actions like sending a text, making a phone call, or playing a song, making Android more accessible to those with speech and motor impairments.
"Looking to the future, the next big step will be for the very concept of the ‘device’ to go away.
Sundar Pichai – Google CEO2
Why Now?
The COVID-19 pandemic made everyone more cautious about touching anything, particularly in public places such as train stations and grocery stores, and this accelerated demand for touchless technologies in places where screens or devices must be shared. Some predicted customer and employee interfaces would quickly be transformed into touchless experiences.
Two years on, that transformation hasn’t quite happened.
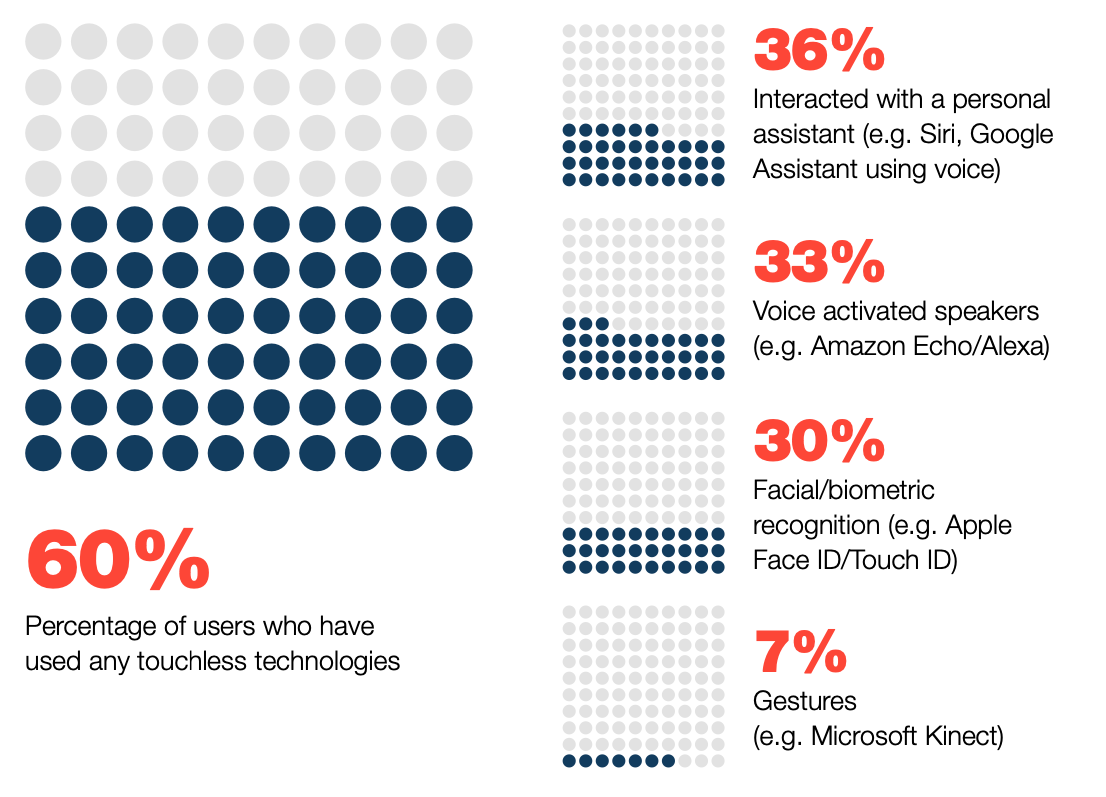
The use of personal assistants has increased, but still only 36% of consumers in our study believe they have ever interacted with one using their voice.
Ask people what they use assistants for, and the use cases are mostly limited to weather checks, playing music, and basic question-answering. In the background, however, things are changing.

Advances in conversational AI are enabling more natural conversations between humans and intelligent devices, with Google Assistant beginning to understand the imperfections of human speech, including pauses, “umms,” and other interruptions.3 Financial organizations are introducing biometric banking, so we can identify ourselves and perform account management tasks using facial or voice recognition.
More and more products are using gesture recognition – from earphones that respond to gestures by enabling ambient sound to infotainment systems that can be touchlessly controlled while driving – but adoption remains low.
The pandemic crystalized the value proposition of touchless technologies, accelerating their development and deployment. In 2023 we’ll see these touchless interfaces gain ground in everyday use. Facial and voice recognition, already the standard for unlocking smartphones, will become the norm for unlocking everything from smart home devices to vehicles and will start to feature intuitive controls that better understand us and deliver more natural experiences and conversations.
Adoption of intuitive technology by US and UK consumers
Analysis - Consumer View
Consumers are already comfortable interacting with personal devices such as smartphones or smart speakers through zero-touch, intuitive interfaces
There are those who happily rely on facial recognition to open their smartphones, tablets, and apps, and can’t imagine life without digital assistants like Google Assistant and Siri performing simple tasks like setting their alarm or calling a taxi. Our survey shows 30% of consumers use tools like FaceID to unlock their devices, and 36% of consumers have interacted with personal assistants like Google Assistant or Apple’s Siri. Unsurprisingly, younger consumers are much more likely to use these interfaces, with usage rising to 55% and 52% for facial recognition and digital assistants, respectively.
While the people regularly using these individual technologies might be in the minority, the important thing is they are extremely positive about them. Overall, 51% of consumers believe using intuitive interfaces can save them time, but this soars to 87% for those using gesture recognition on a weekly basis. Similarly, just 33% of consumers who haven’t used intuitive interfaces believe they can help reduce screen time when interacting with brands, but this rises to 77% for those using gesture-based interfaces on a weekly basis.
This perspective extends beyond interactions with their own devices. Over half of consumers already using these technologies want to see brands deploying intuitive interfaces to improve the customer experience.
There is one clear message here. The 40% of people who have not used intuitive technologies are largely uninterested in them – just 19% would like to see brands adopt more intuitive interfaces to improve their experience. Those who have used them see their value and want brands to embrace them – 89% of those who use gestures want to see brands adopt more intuitive interfaces to improve the customer experience.

Analysis - Company View
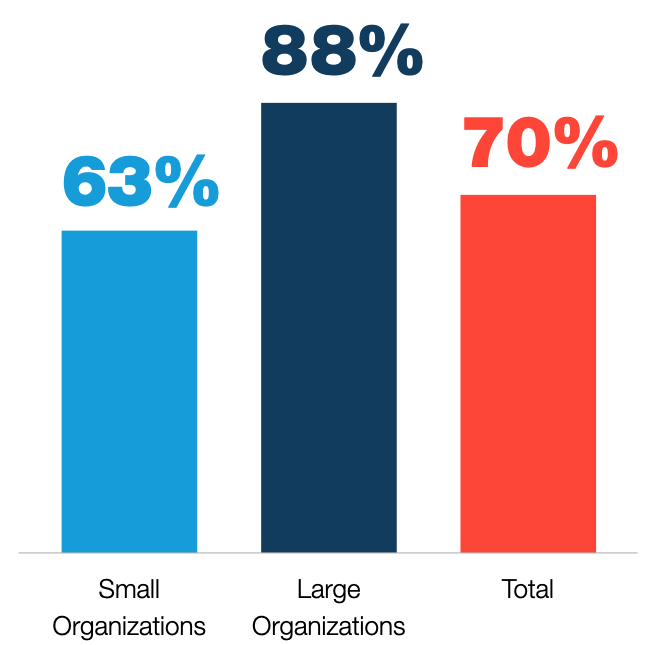
Businesses are positive about the opportunities intuitive technologies present – 70% are planning to offer more intuitive ways to interact with customers, rising to 88% for larger businesses.
There are several reasons for this positive sentiment. First and foremost is the potential to enhance the customer experience, with 61% of US businesses believing intuitive interfaces will enable them to deliver more seamless, responsive, and personalized experiences. From integrating online platforms with smart speakers to support voice-based shopping to enabling users to pay with the unique signature of their palm,4 businesses understand these new interfaces will help customers interact with their products and services in more natural, intuitive ways.
A second driver of the positive sentiment around intuitive technologies is the potential for businesses to collect more first-party data and better understand their customers.
Overall, 53% of businesses see this as a potential benefit, rising to 70% of businesses in the financial services sector, where the ability to understand the needs of individual customers and meet them with relevant products or services appears to be particularly important.
Finally, businesses are convinced specific aspects of intuitive technology, such as digital identity verification through facial or voice recognition, have the potential to both enhance security and improve acquisition. They enable businesses to onboard customers more rapidly and reduce drop-off during the onboarding process.
Given this wide range of possible benefits, most businesses expect intuitive technologies to give them a competitive boost. 64% of large businesses believe intuitive interfaces will become a source of competitive advantage for consumer-facing businesses in the next five years. And for retail businesses this rises to 74%.
Businesses are looking to offer more intuitive ways for their customers to interact with them
Where next?
The first generation of assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Cortana helped to increase acceptance of voice user interfaces
Today, using smart speakers and speech recognition for online search queries doesn’t seem nearly as futuristic as it did 10 years ago.
But the new era of voice user interface is only just beginning, and ongoing advances in AI and NLP will enable us to have ever-more natural, fluid conversations with these digital assistants. Next-generation interfaces will leverage an array of sensors to add context to gaze, motion, and voice, and will be able to perform increasingly complex, multi-step tasks with ease.
As technological development continues, use cases will proliferate, and so too will deployments. The voice interface market is forecast to double in size by 2027, by which time it will be worth $46 billion.5
Similarly, the evolution of sensing, signal processing, and AI is creating more intelligent systems capable
of recognizing increasingly complex motions and gestures. Advanced gesture control will penetrate new markets, enabling intuitive interfaces in everything from smart navigation and consumer electronics to gaming and healthcare. As with voice interfaces, the gesture interface market is expected to experience significant growth, doubling in size to reach $25 billion by 2026.6
The gesture interface market is expected to experience significant growth, doubling in size by 2026 to reach
But the potential of intuitive technologies isn’t just limited to voice and gesture-based interfaces. Biometrics, including facial recognition, will reduce our reliance on physical documents for identity verification and will open possibilities for new, intuitive, and secure ways to prove we are who we say we are online.
Intuitive interfaces will transform how we interact with brands across both physical and digital channels. As we step toward the metaverse, these interfaces will enable the virtual worlds around us to understand us and our intentions intuitively, enabling brands to deliver personalized experiences that adapt and respond to our every need, all without touching a screen or device.
Immersive Shopping
Immersive shopping uses simulation-based technologies such as augmented and virtual reality to create interactive and highly personal shopping experiences.
Related Resources
References
Sources
- blog.google. Two new tools that make your phone even more accessible.
- time.com Google CEO’s new letter on the company’s future.
- blog.google. Have more natural conversations with Google Assistant.
- one.amazon.com. How it works.
- globenewswire.com. The worldwide voice user interface industry is expected to reach $45.9 billion by 2027.
- businesswire.com. Global gesture recognition market trajectory & analytics report 2022.
Figure Data
Organization Size Graph - Source: MTM/Acxiom – CX Trends for 2023 – B2B Survey. Question: To what extent do you agree with each of the following statements about zero user interface technology? Base: Total n = 200, small organization n = 75, large organization n = 50.